Hi, Dave here from Starscape SEO. Google Merchant Center is an essential tool for any e-commerce business looking to showcase products on Google Shopping.
There are several ways to upload your product feed to Google Merchant Center, each with its own advantages and potential drawbacks.
This article will explore three primary methods: directly uploading products, using dynamic feeds via e-commerce platforms and plugins, and syncing a Google Sheet.
We’ll also cover the necessary attributes, which ones are required and which aren’t, and how your feed can impact your product library and Google’s display of your products.
Directly Uploading Products
Pros
Control and Precision:
Directly uploading your products gives you full control over the data you submit to Google Merchant Center. This method is particularly useful if you have a smaller product catalog or if you want to ensure every detail is accurately represented.
Simplicity:
If your inventory is not frequently updated, direct uploads can be straightforward and require minimal ongoing management.
Cons
Manual Effort:
For larger inventories, manually uploading products can become cumbersome and time-consuming. Each product must be updated individually, making it impractical for businesses with extensive or frequently changing catalogs.
Risk of Errors:
Manual entry increases the risk of errors, such as missing attributes or incorrect data, which can result in product disapprovals by Google.
Uploading Dynamic Feeds via Platforms and Plugins

Pros
Automation: Dynamic feeds allow for automatic updates, which is crucial for businesses with large or frequently changing inventories. Platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento offer built-in or plugin-based solutions that sync your product data with Google Merchant Center automatically.
Scalability: This method is ideal for larger businesses, as it can handle thousands of products without manual intervention. Any changes in your e-commerce platform are automatically reflected in your Google Merchant Center feed.
Comprehensive Data Management: Plugins and platform integrations often include advanced features, such as automatic attribute mapping and error checking, to ensure your feed is optimized and compliant with Google’s requirements.
Cons
Complexity: Setting up dynamic feeds can be more complex than direct uploads, especially if you’re dealing with customizations or non-standard products. Ensuring the correct configuration of attributes and settings can require a learning curve.
Dependency on Third-Party Tools: Relying on plugins or third-party integrations can sometimes lead to issues, such as syncing errors or limitations in customization. Additionally, these tools may come with associated costs.
Platforms and Plugins
Shopify: Offers built-in Google Shopping integration that simplifies the process of syncing your product feed.
WooCommerce: Plugins like “Google Listings & Ads” or “Product Feed PRO for WooCommerce” provide seamless integration with Google Merchant Center.
Magento: Extensions like “Google Shopping Feed” enable automated feed generation and syncing with Google Merchant Center.
Syncing a Google Sheet
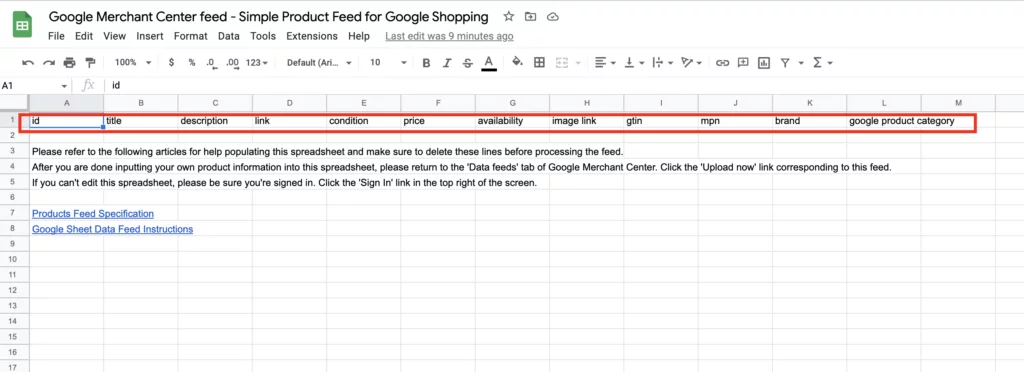
Pros
Flexibility: Google Sheets allow for easy editing and updating of product data, making it an excellent option for businesses that prefer a spreadsheet interface. You can customize your feed as needed and update it regularly.
Cost-Effective: Syncing a Google Sheet is a free method that doesn’t require expensive plugins or third-party tools.
Collaboration: Multiple team members can collaborate on the same sheet, making it easier to manage and update product data.
Cons
Manual Maintenance: Although easier than direct uploads, maintaining a Google Sheet can still be labor-intensive, especially for large inventories. Regular updates are necessary to keep your feed accurate.
Risk of Inconsistencies: If not managed carefully, data inconsistencies can arise, leading to errors in your product feed and potential disapprovals by Google.
Attributes: What You Need and What You Don’t
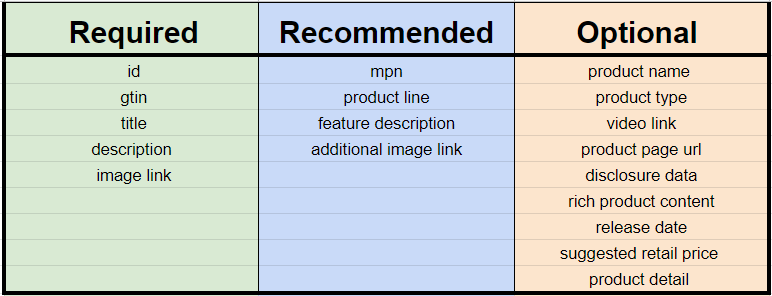
When uploading your product feed, certain attributes are mandatory, while others are optional but recommended for better visibility and performance on Google Shopping.
Here’s a breakdown:
Required Attributes
- ID: A unique identifier for each product.
- Title: A clear and concise name of the product.
- Description: A detailed description that accurately represents the product.
- Link: The URL of the product page on your website.
- Image Link: The URL of the product image.
- Price: The product’s price, including any applicable taxes.
- Availability: The product’s stock status (in stock, out of stock, pre-order).
- Brand: The brand name of the product.
- GTIN: Global Trade Item Number (such as UPC, EAN, ISBN).
Optional (but Recommended) Attributes
- Product Type: Helps in categorizing the product within your website.
- Google Product Category: Maps the product to Google’s predefined categories.
- Sale Price: If the product is on sale, this attribute can be used to show the discounted price.
- Shipping: Specify shipping costs if they vary by region or product.
Not Needed (But May Be Useful)
- Additional Images: While not required, adding more images can enhance the product’s appeal.
- Custom Labels: Useful for creating custom campaigns or filtering products within Google Ads.
How Your Feed Affects Your Product Library
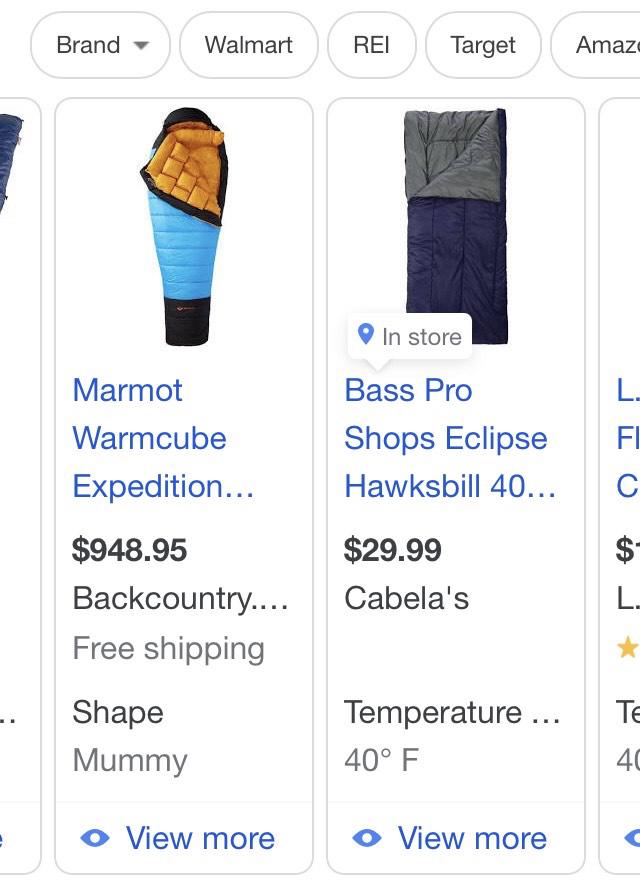
The accuracy and completeness of your product feed directly impact how Google indexes and displays your products.
Google uses the data in your feed to match your products with relevant search queries. Here’s how your feed can affect your product library:
Visibility: A well-optimized feed ensures your products are more likely to appear in relevant search results. Missing or incorrect attributes can lead to your products being excluded from Google Shopping.
Ad Performance: The attributes in your feed influence how your products are presented in Google Ads. Accurate and detailed feeds typically result in better ad performance and higher click-through rates.
Customer Experience: Inaccurate feeds can lead to a poor customer experience, such as displaying incorrect prices or out-of-stock items, which can harm your reputation and lead to lost sales.
Conclusion
Choosing the right method to upload your product feed to Google Merchant Center depends on your business size, inventory complexity, and technical resources.
Direct uploads offer control for small catalogs, dynamic feeds via platforms and plugins provide automation for large inventories, and syncing a Google Sheet offers flexibility for those comfortable with spreadsheets.
Ensuring your feed is accurate, complete, and well-optimized is crucial for maximizing visibility and sales on Google Shopping.

Call or Text Starscape SEO: (519) 208-8680


