Hi, Dave Fox here from Starscape SEO. Today I want to talk about a topic near and dear to my heart, and that is Search Console Googlebot crawl requests, which I use frequently to send Google a message that I have new URL’s that I’d like it to index.
In case you don’t know, Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, is responsible for discovering and indexing content on the internet.
Google, as you may know, is one big index, or catalog, and one of its primary functions is to serve up content to users seeking specific information, whether it be the surface area of the sun, or where you can get a milkshake at 2am.
This content comes in the form of websites, or information it pulls from websites. Even A.I. such as Gemini, if you didn’t know, is just Google’s clever way of repackaging pre-existing information that it quickly grabs and re-phrases using large language models, but that’s another story.
By understanding how Googlebot operates and how to request a crawl, you can optimize your website’s visibility in search results.

Call or Text Starscape SEO: (519) 208-8680

What is a Googlebot Crawl Request?
A Googlebot crawl request is a signal sent to Google indicating that you’d like your website to be crawled or re-crawled by Googlebot.
This can be particularly useful when you’ve made significant changes to your website, such as adding new content or updating existing pages.
Or else, maybe your website has never been crawled, and you have just generated your site’s first xml sitemap (not to be confused with html sitemaps). In this case, I recommend you get Search Console fired up and get that first invitation to Googlebot sent out so that Google knows you have content you want to be in everyone’s favourite information mega-resource – Google’s very own search results.
Why Request a Crawl?

I basically just told you, but let’s say it again, put nicely and succinctly.
New Content: When you add new content to your website, requesting a crawl ensures that Googlebot is aware of the changes and can index the new pages.
Updates: If you’ve made significant updates to existing pages, such as modifying the content or structure, a crawl request can help Googlebot re-evaluate the page’s relevance and ranking.
Technical Issues: If you’ve resolved technical issues that may have been preventing Googlebot from crawling your website effectively, requesting a crawl can help ensure that the issues have been addressed.
Sitemap Updates: If you’ve updated your sitemap, a crawl request will notify Googlebot of the changes and help it discover new pages.
How to Request a Crawl
There is basically one way to do this and one way only and here it is!
Access Search Console: Log in to your Google Search Console account.
Select Your Property: Choose the website you want to request a crawl for.
Navigate to the “URL Inspection” Section: Click on the “URL Inspection” tab in the left-hand navigation menu, or it’s also right there at the top.
Enter the URL: Enter the URL of the page you want Googlebot to crawl.
Fetch: Click the “Request Indexing” button to initiate the crawl.
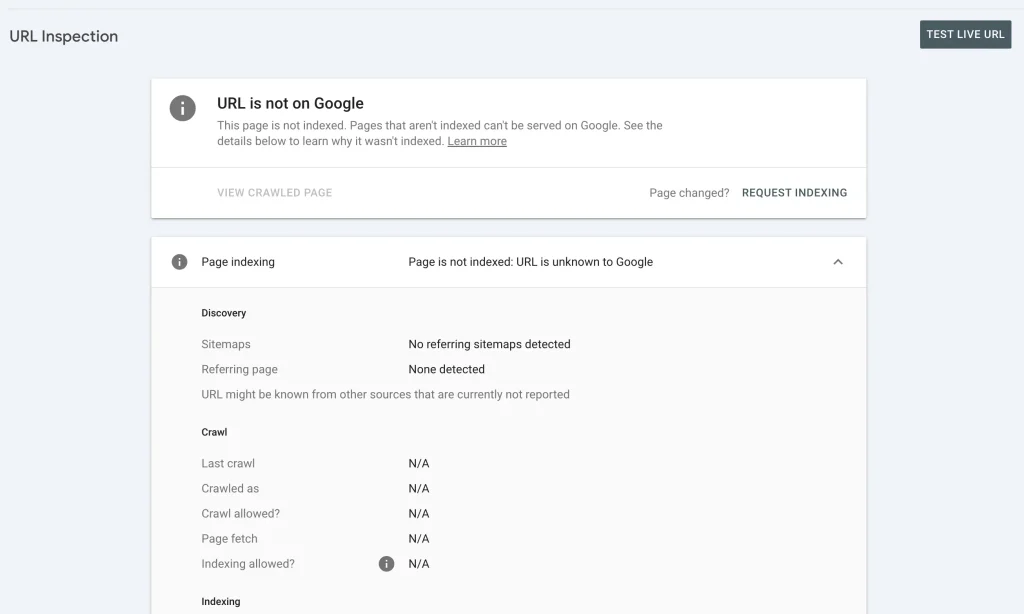
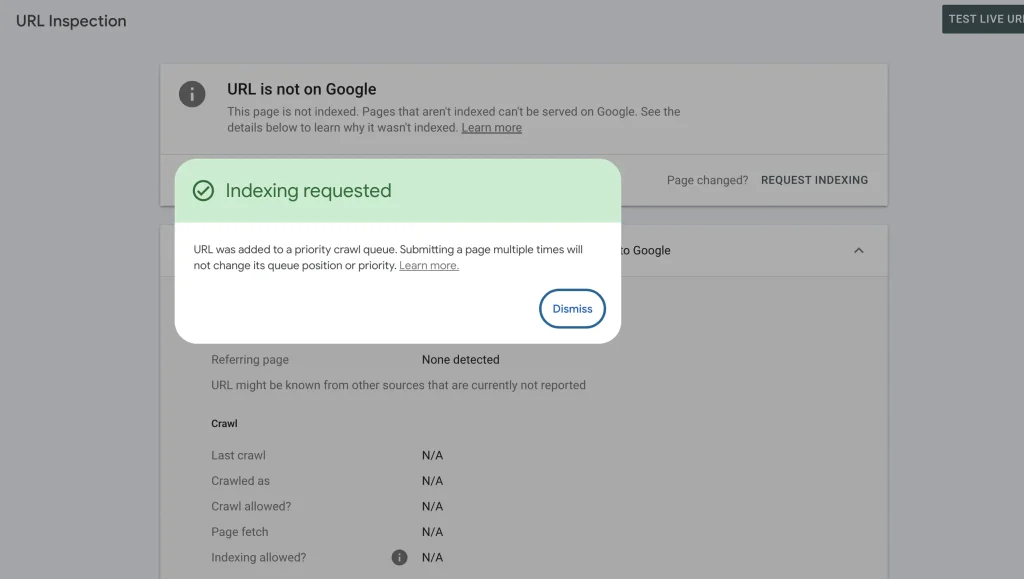
If the URL is not recognized by Google, this means it’s all the more important to request that crawl, so that it ensures Googlebot does at some point pay your URL a visit.
The url can be any URL that’s part of your domain, including, and especially, the “root” domain (the main url).
Factors Affecting Crawl Frequency

Several factors influence how often Googlebot crawls your website, including:
Website Importance: More important websites are typically crawled more frequently.
Website Size and Structure: Larger and more complex websites may require more frequent crawling.
Changes to the Website: Websites with frequent updates are more likely to be crawled more often.
Technical Issues: Websites with technical issues that hinder crawling may be crawled less frequently.
Best Practices for Crawl Requests

Prioritize Important Pages: Focus on requesting crawls for pages that are most important to your website’s success.
Submit a Sitemap: Provide Googlebot with a sitemap to help it discover new pages and prioritize crawling.
Address Technical Issues: Ensure your website is free of technical errors that could hinder crawling.
Promote Your Content: Share your content on social media and other platforms to increase visibility and potentially attract more backlinks.
Avoid Excessive Requests: While it’s okay to request crawls occasionally, avoid making excessive requests, as this can be seen as spammy behavior.
Understanding Search Console’s Crawl Stats
Search Console’s Crawl Stats provide valuable insights into how Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, is interacting with your website.
This data can help you identify potential issues and optimize your website for better search engine visibility.
Key Metrics in Crawl Stats
Total Crawled URLs: The total number of pages Googlebot has crawled on your website during the selected time period.
Pages with Errors: The number of pages that encountered errors during the crawling process. These errors can include issues like server errors, broken links, or content that is inaccessible to Googlebot.
Crawl Rate: The average number of pages Googlebot crawls per day. This can help you understand how frequently Googlebot is visiting your website.
Crawl Errors: Detailed information about specific errors that occurred during the crawling process, such as HTTP status codes.
Blocked URLs: The number of URLs that were blocked from crawling due to robots.txt instructions or other restrictions.
How to Interpret Crawl Stats
High Crawl Rate: A high crawl rate generally indicates that Googlebot is actively exploring your website and indexing its content.
Low Crawl Rate: A low crawl rate may suggest that there are issues preventing Googlebot from crawling your website efficiently.
High Error Rate: A high error rate can negatively impact your website’s visibility in search results. It’s important to investigate and address these errors promptly.
Blocked URLs: Ensure that your robots.txt file is configured correctly to allow Googlebot to crawl the pages you want to be indexed.
Optimizing Crawl Stats

Submit a Sitemap: Provide Googlebot with a sitemap to help it discover new pages and prioritize crawling.
Fix Technical Issues: Address any errors or technical problems that may be hindering Googlebot’s ability to crawl your website.
Improve Website Speed: A faster website load time can improve user experience and encourage Googlebot to crawl your site more frequently.
Optimize Content: Create high-quality, relevant content that is easy for Googlebot to understand and index.
By regularly monitoring and analyzing your Crawl Stats in Search Console, you can identify potential issues and take steps to improve your website’s search engine visibility.
Conclusion
By understanding the importance of Googlebot crawl requests and following best practices, you can optimize your website’s visibility in search results.
By proactively requesting crawls, you can ensure that Googlebot is aware of your website’s changes and can index your content effectively.

