Hi, Dave Fox here from Starscape SEO. So, you’ve seen it everywhere—www at the front of websites like www.example.com. But the real question is, do we even need it anymore? And was there ever a point to it in the first place? Spoiler alert: there was!
Why We Had www in the First Place
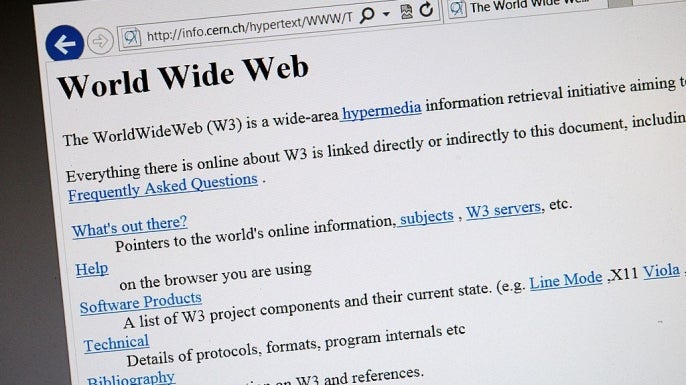
Back in the early, exciting days of the internet, www wasn’t just a pretty prefix. It served an actual purpose.
Think of it like an organizational label. In the early internet, there were all sorts of services running on domains, not just websites. There was email, file transfer protocols (FTP), and other types of data traffic.
So, the “www” prefix came into play as a subdomain to say, “Hey, this is the part of the domain that’s specifically for the web! You’re here to browse!”
For example:
ftp.example.com would handle your file transfers.
mail.example.com managed your emails.
And, of course, www.example.com meant “This is the web version!” Easy peasy, right?
But it wasn’t just about clarity for people—it was also a technical thing. Servers were set up to treat these subdomains separately to help spread out the load. It was a way to manage the growing web more efficiently.
Was It Really Necessary?

Back then, yes! The internet wasn’t the all-consuming web we know today. There were lots of other protocols flying around, and www made sense to keep everything tidy and in its lane.
But as the internet evolved and the web became the superstar of the show, that distinction became… let’s say, less important.
Today, most websites don’t really need to use the www subdomain. You can just type example.com, and boom—you’re there. It’s all thanks to the magic of DNS (Domain Name System) and better, faster servers.
So, Do We Need www Anymore?
Nope, not really! These days, www is mostly just cosmetic. It’s more of a style choice than a technical requirement.
In fact, many big-name brands have completely dropped the www for a cleaner, more modern look. example.com works just as well as **www.example.com**—because modern web browsers know what you mean without needing to be told “Hey, I’m on the web!”
But Was It Just for Looks?

At first, www had a true, practical reason to exist. It was functional!
But now, with web technology and server capabilities being light years ahead of where they were when the internet began, www has become a bit of an optional relic.
Some companies still use it for tradition, but it’s definitely no longer a must-have.
www and SEO
When it comes to SEO and the decision of using “www” or not, it’s more important than you might think, especially when you’re setting up your domain in Google Search Console.
Here’s the lowdown on how www can affect your website’s SEO and why you should pay attention to your domain setup.
From a user’s perspective, it might not seem like a big deal whether your website is www.example.com or just example.com.
But in the eyes of search engines, these are considered two different URLs. This distinction can affect your SEO if not handled properly, and here’s why.
Consistency is Key: Canonical URLs

When Google crawls your site, it wants to know which version of your domain to treat as the “canonical” version, meaning the primary version that should be indexed and ranked.
If both the www and non-www versions of your site exist and are accessible, Google might treat them as two different websites with duplicate content.
This can lead to splitting your SEO efforts between the two versions, which means:
- Your backlinks might get divided between www.example.com and example.com.
- Your traffic might get split.
- Your search rankings can get affected since Google prefers to know which version is the “official” one.
To avoid this, it’s crucial to choose one version (www or non-www) and stick with it for consistency.
Registering Your Domain in Google Search Console
When you register your domain in Google Search Console, you’ll be asked to specify whether you want to track the www version, the non-www version, or the entire domain. Here’s what you need to consider:
Single Version (www or non-www): If you pick one specific version (e.g., www.example.com), that’s the one Google will crawl and rank. However, it’s essential that you redirect the other version (non-www) to this one to avoid duplicate content issues.
Domain-Wide Setup: The domain property option covers all variations of your domain (www, non-www, HTTP, HTTPS). This option is helpful if you’ve just launched your site and want to cover all your bases. However, you still need to set one version as the preferred domain for Google.
Redirects and Consistency
Whichever version you decide on (www or non-www), make sure that:
- You set up 301 redirects from one version to the other.
- This ensures that if someone types in example.com, they automatically get sent to www.example.com (or vice versa).
- It also tells Google which version is the primary one, keeping your SEO efforts consolidated and effective.
Does www Help or Hurt SEO?
There’s no inherent SEO advantage to using www versus non-www. The key is consistency and ensuring that whichever version you choose is properly redirected and identified as the canonical version.
If not done correctly, it can lead to issues like split ranking power and duplicate content, which can hurt your SEO.
In short, www isn’t about boosting your rankings but making sure your site is correctly understood and crawled by search engines. Just pick one, stick with it, and ensure everything is properly redirected!
That’s All, Folks!
So there you have it—the full story of www! It started with a purpose, but now, it’s more of a nostalgic nod to the internet’s roots. Whether you include it or not is totally up to you!

