Hi, Mahmudul Hasan here from Starscape SEO. In today’s digital age, security is one of the most important factors for any online business or website.
As more transactions, interactions, and data exchanges happen on the web, ensuring that these exchanges are secure becomes critical.
That’s where SSL certificates come into play.
Whether you’re running an e-commerce site, a blog, or a corporate website, SSL certificates are vital for protecting sensitive information and gaining the trust of your users.
Across industries, businesses and website owners are frequently searching for terms like “SSL certificate for websites” and “how to secure my website with SSL” as they look to enhance their website’s security and performance.
But what exactly is an SSL certificate, and how does it benefit your website?
In this article, we’ll break down what an SSL certificate is, explore how it works, why it’s essential for any website, and how you can improve your site’s security and trustworthiness by implementing it.
What is an SSL Certificate?
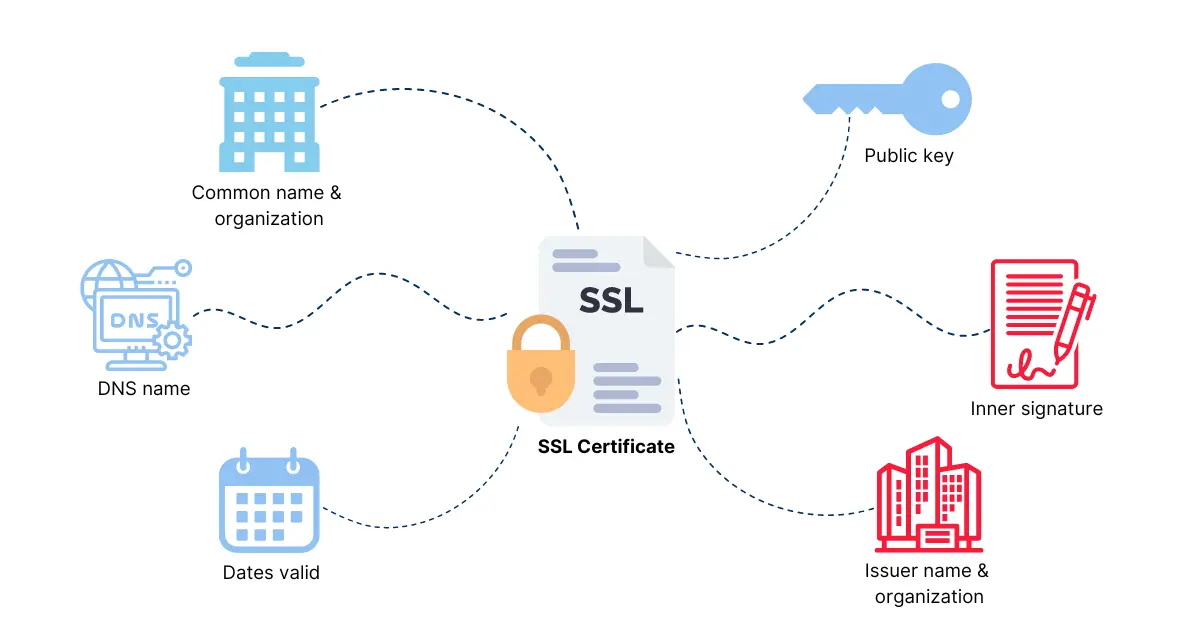
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables encrypted connections between the server and the user’s browser.
Essentially, it ensures that any data transmitted between the website and the visitor remains private and secure.
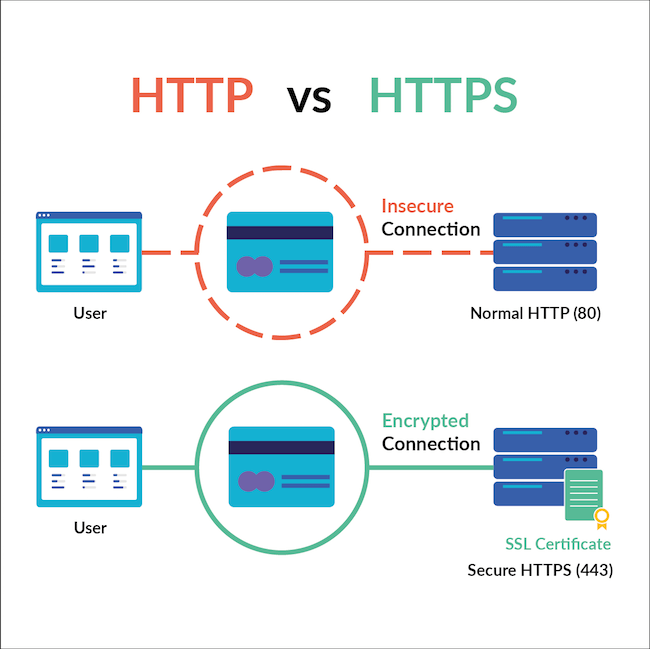
When an SSL certificate is installed on a website, the URL changes from “http://” to “https://,” where the “s” stands for “secure.”
SSL certificates are used to protect sensitive data such as credit card numbers, personal information, login credentials, and more.
They play a crucial role in protecting against cyber threats like data breaches, man-in-the-middle attacks, and phishing scams.
Beyond security, SSL certificates also impact a website’s SEO and user experience, making them a must-have for any modern site.
How Does an SSL Certificate Work?
SSL certificates work by creating a secure, encrypted connection between the web server and the user’s browser. Here’s how the process unfolds:
SSL Handshake
When a user visits a website with SSL, the browser requests the SSL certificate from the server.
Authentication
The web server sends a copy of its SSL certificate to the browser. The browser then checks the certificate to ensure that it’s valid and issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
Session Keys
If the certificate is trusted, the browser and the server generate session keys, which are unique encryption keys for that session. These keys are used to encrypt and decrypt the data exchanged during the session.
Secure Connection
Once the handshake is complete, all communication between the browser and the server is encrypted, ensuring that sensitive data is protected from interception.
This encryption ensures that any information exchanged between the visitor and the website cannot be read or tampered with by unauthorized third parties.
Why is an SSL Certificate Important?
Now that you understand what an SSL certificate is and how it works, let’s explore why it’s so important for businesses and websites:
Data Security
The most obvious benefit of an SSL certificate is the security it provides.
SSL encryption protects sensitive information such as credit card numbers, passwords, and personal details from being intercepted by hackers.
This is particularly crucial for e-commerce websites, online payment systems, and any site that collects user data.
Without an SSL certificate, data is transmitted in plain text, making it easy for attackers to intercept and misuse this information.
SSL ensures that data is encrypted and only accessible by the intended recipient.
Builds Trust and Credibility
In a world where cybercrime is on the rise, consumers are increasingly concerned about the security of their online interactions.
SSL certificates play a vital role in building trust with your audience.
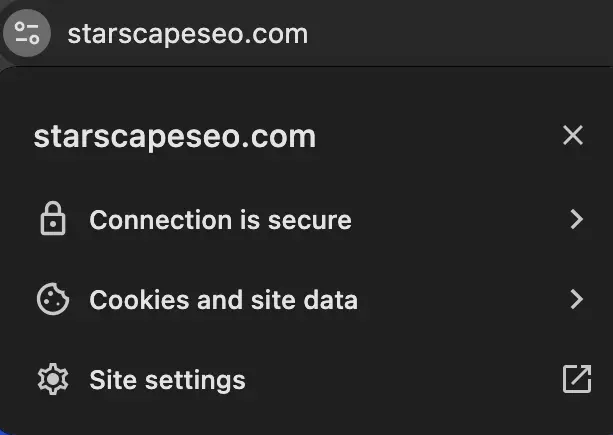
When visitors see that a website has an SSL certificate (indicated by the padlock icon next to the URL), they feel more confident that their personal information is safe.
Conversely, if a website lacks SSL, browsers may display a “Not Secure” warning, which can deter potential customers and damage your credibility.
Having an SSL certificate reassures users that your website is legitimate, secure, and trustworthy.
Improves SEO Rankings
Did you know that SSL certificates can also impact your website’s SEO performance?
In 2014, Google announced that HTTPS (SSL-secured websites) would be used as a ranking signal.
This means that websites with SSL certificates are more likely to rank higher in search engine results compared to non-secure websites.
Google prioritizes user safety, and as a result, it favors websites that take security seriously.
By implementing SSL, you not only protect your site and users but also gain a competitive edge in SEO.
Ensures Compliance with Data Regulations
In many industries, particularly those dealing with sensitive personal data (e.g., healthcare, finance), compliance with data protection regulations is mandatory.
Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for payment processors require businesses to use encryption methods like SSL to protect customer data.
Failing to comply with these regulations can result in severe fines and penalties, so having an SSL certificate is crucial for legal compliance.
Enables Secure Online Payments
If you’re running an e-commerce website, SSL certificates are a must-have for secure online transactions.
Payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, and others require websites to use SSL certificates to process payments.
Without one, your customers’ payment information would be at risk, and your website might not be able to accept payments at all.
Moreover, SSL encryption helps prevent fraud and ensures that your customers can make secure transactions with peace of mind.
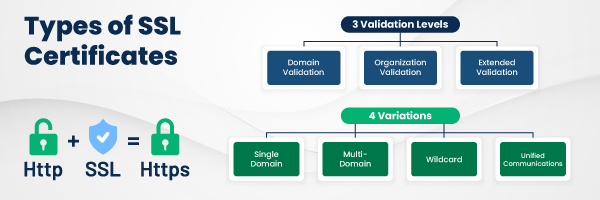
Types of SSL Certificates
SSL certificates come in different types, depending on the level of validation and the number of domains they cover.
Here are the main types:
Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificate
The most basic type of SSL, DV certificates verify only the ownership of the domain.
They provide basic encryption but don’t require extensive identity verification.
Organization Validated (OV) SSL Certificate
This type of certificate provides a higher level of validation by verifying the organization’s identity.
It’s ideal for businesses that want to establish greater trust with users.
Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificate
EV certificates offer the highest level of validation and security.
They require a rigorous vetting process and are often used by large enterprises, banks, and financial institutions.
Wildcard SSL Certificate
A wildcard SSL certificate allows you to secure a primary domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate.
It’s useful for businesses with multiple subdomains (e.g., blog.example.com, shop.example.com).
How to Get an SSL Certificate
Getting an SSL certificate for your website is simple. Follow these steps:
Choose a Certificate Authority (CA)
Select a trusted CA like Let’s Encrypt (free) or paid services such as DigiCert, Comodo, or GoDaddy.
Generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request)
This is a code that you generate from your server, which is then sent to the CA.
Install the Certificate: Once you receive your SSL certificate, you’ll need to install it on your website’s server. Many web hosting providers offer free SSL installation services.
Test Your SSL Certificate
After installation, use tools like SSL Labs to test your SSL certificate and ensure it’s working correctly.
Final Thoughts
An SSL certificate is no longer optional—it’s a fundamental requirement for any website. It secures data, builds trust with users, improves SEO, ensures compliance, and enables secure payments.
By implementing SSL, you protect your website and provide a safer experience for your users, ultimately boosting your online reputation and performance.